GatewayAPI
Gateway API is an official Kubernetes project focused on L4 and L7 routing in Kubernetes. This project represents the next generation of Kubernetes Ingress, Load Balancing, and Service Mesh APIs. From the outset, it has been designed to be generic, expressive, and role-oriented.
The overall resource model focuses on 3 separate personas and corresponding resources that they are expected to manage:
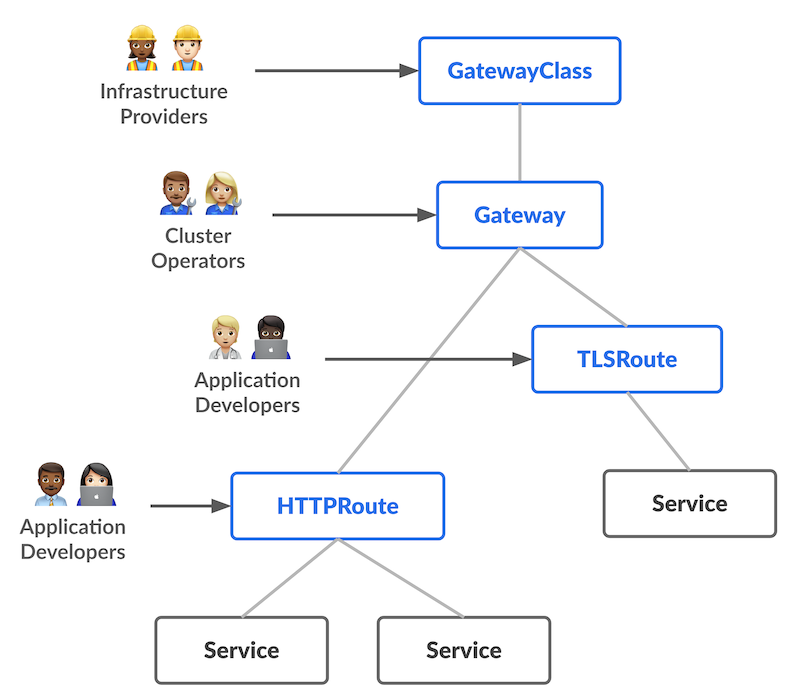
Most of the configuration in this API is contained in the Routing layer. These protocol-specific resources (HTTPRoute, GRPCRoute, etc.) enable advanced routing capabilities for both Ingress and Mesh.
TOC
Gateway API for Ingress
When using Gateway API to manage ingress traffic, the Gateway resource defines a point of access at which traffic can be routed across multiple contexts -- for example, from outside the cluster to inside the cluster (north/south traffic).
Each Gateway is associated with a GatewayClass, which describes the actual kind of gateway controller that will handle traffic for the Gateway; individual routing resources (such as HTTPRoute) are then associated with the Gateway resources. Separating these different concerns into distinct resources is a critical part of the role-oriented nature of Gateway API, as well as allowing for multiple kinds of gateway controllers (represented by GatewayClass resources),
Gateway API concepts
The following design goals drive the concepts of Gateway API. These demonstrate how Gateway aims to improve upon current standards like Ingress.
- Role-oriented - Gateway is composed of API resources which model organizational roles that use and configure Kubernetes service networking.
- Portable - This isn't an improvement but rather something that should stay the same. Just as Ingress is a universal specification with numerous implementations, Gateway API is designed to be a portable specification supported by many implementations.
- Expressive - Gateway API resources support core functionality for things like header-based matching, traffic weighting, and other capabilities that were only possible in Ingress through custom annotations.
- Extensible - Gateway API allows for custom resources to be linked at various layers of the API. This makes granular customization possible at the appropriate places within the API structure.
Some other notable capabilities include:
- GatewayClasses - GatewayClasses formalize types of load balancing implementations. These classes make it easy and explicit for users to understand what kind of capabilities are available via the Kubernetes resource model.
- Shared Gateways and cross-Namespace support - They allow the sharing of load balancers and VIPs by permitting independent Route resources to attach to the same Gateway. This allows teams (even across Namespaces) to share infrastructure safely without direct coordination.
- Typed Routes and typed backends - Gateway API supports typed Route resources and also different types of backends. This allows the API to be flexible in supporting various protocols (like HTTP and gRPC) and various backend targets (like Kubernetes Services, storage buckets, or functions).
For more detailed descriptions of the Gateway API, please refer to the gateway-api documentation.